According to a BMO study in 2023, the average Canadian believes they need about $1.7 million saved up to retire comfortably.
Another common rule of thumb suggests that you will need about 70% of your pre-retirement household income annually for 25 years post-retirement.
However, individual needs can vary greatly. For the purposes of this discussion, we’ll focus on the first scenario – accumulating $1.7 million.
Given the limitations of space in this column, let’s embark on a simplified, back-of-the-napkin calculation to look at how long it might take to reach that $1.7 million target, assuming various rates of return and investment amounts.
Setting base assumptions
For our retirement planning scenario, we’ll use the mutual fund version of the Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (NYSEMKT:VTI) as our benchmark, utilizing its comprehensive historical data spanning 30 years, back to 1993.
We’ll assume that your investments are made within a Tax-Free Savings Account (TFSA), with an annual contribution limit of $7,000. This limit is fixed for our calculations, though it’s likely to increase in the future.
Our scenario excludes potential accelerators like workplace pension contributions or RRSP matching benefits, which could significantly hasten the growth of your retirement funds. Similarly, we won’t consider income from government programs like the Canada Pension Plan (CPP) or Old Age Security (OAS).
Lastly, we’ll assume that you are an ideal investor: you consistently make your full annual TFSA contribution as soon as you’re allowed, you never panic sell, and you promptly reinvest all dividends received.
The results
If you had started investing in 1993 with an annual contribution of $7,000 to a fund similar to the Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (again, acknowledging that the TFSA didn’t exist then), by the end of April 2024, your investment would have grown to $1,621,233.
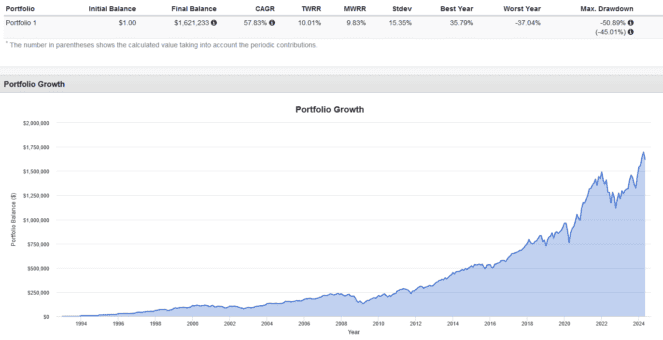
However, when adjusted for inflation, this amount would be equivalent to $736,563 today. This adjustment means that while the nominal dollar amount appears large, the actual purchasing power of this money has been reduced due to the effects of inflation over time.
Regarding your investment’s performance, you achieved a Time-Weighted Rate of Return (TWRR) of 10% and a Money-Weighted Rate of Return (MWRR) of 9.8%.
The TWRR measures the compound rate of growth in your portfolio, assuming any cash flows (like your contributions) don’t affect the portfolio’s growth rate. It’s useful for comparing the performance of investment managers.
The MWRR, on the other hand, does consider the timing of cash flows and reflects the actual return earned on the money invested, making it more personalized to an individual investor’s experience.
During the 2008 financial crisis, your investment would have seen a staggering drop of 50.9%, and on average, it would have fluctuated by 13.4% each year, either up or down. This level of volatility is significant but not unexpected given the nature of stock market investments.
Although you made it to nearly $1.7 million, which was the goal, it was a close call. Could there have been a better investment choice?
Possibly, but considering you were invested broadly in the U.S. stock market, your strategy avoided the complexities and risks associated with trying to pick individual stocks, which is notoriously difficult.
To potentially improve results, you could have 1) invested more money, 2) contributed more frequently, or 3) extended your investment period.
The takeaway? Successful investing isn’t just about choosing the right stocks or assets; it’s also about disciplined saving, regular investing, and maintaining good investment behaviours over time.







